Fill Out Your Straight Bill Of Lading Template
The Straight Bill of Lading form plays a crucial role in the transportation and shipping industries, serving as a key document that facilitates the movement of goods from one location to another. This form is primarily used when the cargo is consigned to a specific person or entity, ensuring that only the designated recipient can claim the shipment. Unlike other types of bills of lading, the Straight Bill of Lading is non-negotiable, which means it cannot be transferred or sold to another party. This characteristic provides a level of security for both the shipper and the consignee, as it establishes clear ownership and accountability. Additionally, the form typically includes vital information such as the names and addresses of the shipper and consignee, a detailed description of the goods being transported, and any special instructions related to the handling or delivery of the cargo. Understanding the intricacies of the Straight Bill of Lading is essential for anyone involved in logistics, as it not only streamlines the shipping process but also ensures compliance with legal requirements and reduces the risk of disputes. By grasping its significance, businesses can navigate the complexities of shipping with greater confidence and efficiency.
Similar forms
The Straight Bill of Lading is often compared to a Warehouse Receipt. Both documents serve as proof of ownership and receipt of goods. A Warehouse Receipt is issued by a storage facility, confirming that goods have been stored there. Like the Straight Bill of Lading, it can be transferred, but it generally pertains to goods held in storage rather than in transit. Both documents provide essential information about the goods, including their description and quantity.
Another similar document is the Order Bill of Lading. This document also serves as a receipt for goods and can be used to transfer ownership. However, unlike the Straight Bill of Lading, the Order Bill allows for the transfer of title through endorsement. This makes it more flexible in transactions, particularly in the shipping industry, where goods may change hands multiple times before reaching their final destination.
A Commercial Invoice is another important document in international trade that shares similarities with the Straight Bill of Lading. While the Straight Bill serves as a shipping document, the Commercial Invoice details the transaction between the buyer and seller. Both documents are crucial for customs clearance and can be used to verify the value and quantity of goods being shipped. They work together to facilitate smooth international transactions.
To protect sensitive information during negotiations, ensure you utilize a proper Non-disclosure Agreement template to establish confidentiality between parties involved.
The Packing List is also comparable to the Straight Bill of Lading. It provides detailed information about the contents of a shipment, including item descriptions, quantities, and weights. While the Packing List is not a legal document like the Straight Bill, it complements it by ensuring that all items are accounted for during transit. This helps prevent disputes and ensures that the recipient receives the correct goods.
A Delivery Order is another document related to the Straight Bill of Lading. It instructs the carrier to deliver goods to a specified party. While the Straight Bill of Lading serves as a title document, the Delivery Order is more of a directive. Both documents are essential for the release of goods but serve different functions in the shipping process.
The Certificate of Origin is similar in that it is often required for customs clearance. This document certifies the country of origin of the goods being shipped. While the Straight Bill of Lading focuses on the transportation of goods, the Certificate of Origin provides important information that can affect tariffs and trade regulations. Both documents play critical roles in international shipping.
A Pro Forma Invoice can also be likened to the Straight Bill of Lading. This document outlines the terms of a sale before the actual transaction takes place. It serves as a preliminary bill, giving the buyer an idea of what to expect. While the Straight Bill of Lading is issued after the shipment, both documents are integral to the sales process, helping to clarify terms and conditions.
Lastly, the Freight Bill is similar in that it details the charges associated with transporting goods. It serves as a request for payment from the carrier to the shipper. While the Straight Bill of Lading focuses on the shipment itself, the Freight Bill provides a financial aspect to the transaction. Both documents are essential for the successful completion of shipping arrangements.
Form Specifications
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A Straight Bill of Lading is a document issued by a carrier that serves as a receipt for goods and a contract for transportation. It indicates that the goods are to be delivered to a specific person. |
| Non-Negotiable | This type of bill of lading is non-negotiable, meaning it cannot be transferred to another party. The named consignee is the only person who can claim the goods. |
| Governing Law | The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) governs the use of bills of lading in most states, ensuring consistency in handling and enforcing these documents. |
| Key Components | A Straight Bill of Lading typically includes details such as the names of the shipper and consignee, a description of the goods, and the shipping terms. |
| Usage | Often used in transactions where the buyer and seller have a trusted relationship, a Straight Bill of Lading simplifies the shipping process by reducing paperwork. |
| Legal Implications | By signing the Straight Bill of Lading, the carrier agrees to transport the goods as specified. Failure to comply can lead to liability for damages or loss. |
Different PDF Templates
What Is I-9 - The form may be necessary for securing a mortgage.
The process of requesting settlement mediation in Georgia is significantly streamlined by the use of the Georgia WC-100 form, which is essential for effective communication between employees and employers regarding workers' compensation claims. For further details on the necessary documentation, you can refer to the Georgia PDF Forms that provide additional resources to aid in the completion of this important form.
Principal Immigrant Meaning - The I-864 form, also known as the Affidavit of Support, is required for certain family-based immigration applications.
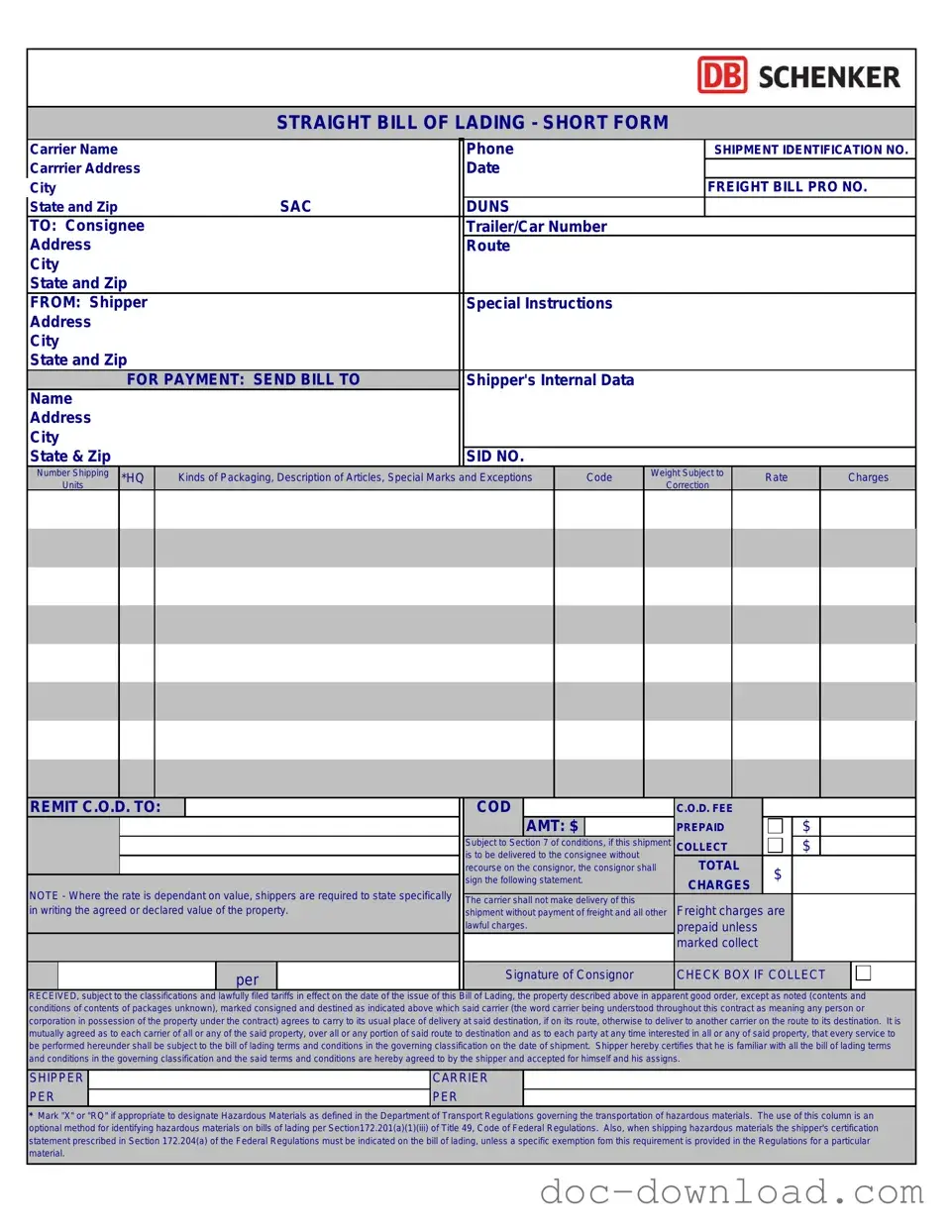
Sample - Straight Bill Of Lading Form
STRAIGHT BILL OF LADING - SHORT FORM
Carrier Name |
|
|
Phone |
|
|
SHIPMENT IDENTIFICATION NO. |
||
Carrrier Address |
|
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
City |
SAC |
|
|
|
|
FREIGHT BILL PRO NO. |
||
State and Zip |
|
DUNS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TO: Consignee |
|
|
Trailer/Car Number |
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
Route |
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State and Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FROM: Shipper |
|
|
Special Instructions |
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State and Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FOR PAYMENT: SEND BILL TO |
|
Shipper's Internal Data |
|
|
|
|
||
Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State & Zip |
|
|
SID NO. |
|
|
|
|
|
Number Shipping *HQ |
Kinds of Packaging, Description of Articles, Special Marks and Exceptions |
Code |
Weight Subject to |
Rate |
Charges |
|||
Units |
|
|
|
|
Correction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REMIT C.O.D. TO: |
|
|
|
|
COD |
|
|
C.O.D. FEE |
|
|
|
|
||
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMT: $ |
|
PREPAID |
|
$ |
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
Subject to Section 7 of conditions, if this shipment |
COLLECT |
|
$ |
|
|
|||
State & Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
is to be delivered to the consignee without |
TOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
recourse on the consignor, the consignor shall |
$ |
|
|
|
|||||
NOTE - Where the rate is dependant on value, shippers are required to state specifically |
|
sign the following statement. |
CHARGES |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
The carrier shall not make delivery of this |
Freight charges are |
|
|
|
|||||||||
in writing the agreed or declared value of the property. |
|
shipment without payment of freight and all other |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lawful charges. |
prepaid unless |
|
|
|
|
||
The agreed or declared vlaue of the property is hereby specifically stated by the shipper to |
|
|
|
|
marked collect |
|
|
|
|
|||||
be not exceeding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
$ |
|
|
|
per |
|
|
Signature of Consignor |
CHECK BOX IF COLLECT |
|
|||||
RECEIVED, subject to the classifications and lawfully filed tariffs in effect on the date of the issue of this Bill of Lading, the property described above in apparent good order, except as noted (contents and conditions of contents of packages unknown), marked consigned and destined as indicated above which said carrier (the word carrier being understood throughout this contract as meaning any person or corporation in possession of the property under the contract) agrees to carry to its usual place of delivery at said destination, if on its route, otherwise to deliver to another carrier on the route to its destination. It is mutually agreed as to each carrier of all or any of the said property, over all or any portion of said route to destination and as to each party at any time interested in all or any of said property, that every service to be performed hereunder shall be subject to the bill of lading terms and conditions in the governing classification on the date of shipment. Shipper hereby certifies that he is familiar with all the bill of lading terms and conditions in the governing classification and the said terms and conditions are hereby agreed to by the shipper and accepted for himself and his assigns.
SHIPPER |
|
CARRIER |
|
PER |
|
PER |
|
*Mark "X" or "RQ" if appropriate to designate Hazardous Materials as defined in the Department of Transport Regulations governing the transportation of hazardous materials. The use of this column is an optional method for identifying hazardous materials on bills of lading per Section172.201(a)(1)(iii) of Title 49, Code of Federal Regulations. Also, when shipping hazardous materials the shipper's certification statement prescribed in Section 172.204(a) of the Federal Regulations must be indicated on the bill of lading, unless a specific exemption fom this requirement is provided in the Regulations for a particular material.