Fill Out Your Profit And Loss Template
The Profit and Loss form, often referred to as the P&L statement, serves as a vital tool for businesses to assess their financial health over a specific period. This document provides a clear overview of revenues, costs, and expenses, enabling business owners and stakeholders to understand how much profit or loss the company has generated. Key components of the form include total revenue, which reflects all income earned, followed by cost of goods sold (COGS), which outlines the direct costs associated with producing goods or services. Operating expenses, including salaries, rent, and utilities, are also detailed, allowing for a comprehensive view of the company's operational efficiency. Additionally, the P&L statement may include non-operating income and expenses, such as interest and taxes, which can significantly impact the bottom line. By analyzing this form, businesses can make informed decisions about budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning, ultimately driving growth and sustainability.
Similar forms
The Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement, shares similarities with the balance sheet. Both documents provide a snapshot of a company's financial health. While the P&L focuses on revenues and expenses over a specific period, the balance sheet presents assets, liabilities, and equity at a single point in time. Together, they help stakeholders understand how well a company is performing and how it stands financially.
The cash flow statement is another document closely related to the P&L. It details the inflow and outflow of cash within a business over a certain period. While the P&L shows profitability, the cash flow statement reveals how well a company manages its cash to fund operations and meet obligations. This distinction is crucial for assessing liquidity and operational efficiency.
The statement of retained earnings complements the P&L by detailing how profits are retained or distributed. It starts with the beginning balance of retained earnings, adds net income from the P&L, and subtracts dividends paid. This document provides insight into how a company reinvests its profits for growth versus distributing them to shareholders.
The budget is similar to the P&L in that it outlines projected revenues and expenses. While the P&L reports actual figures, the budget serves as a plan for future financial performance. Comparing the two can help identify variances and inform strategic decisions, allowing businesses to adjust their operations based on performance against expectations.
To ensure compliance with state regulations and proper operation of your LLC, it is essential to complete an Operating Agreement for your business. This vital document establishes the framework for governance and operational protocols. You can start the process by accessing the required fillable Operating Agreement form at this link: essential fillable Operating Agreement form.
The trial balance is another document that aligns with the P&L. It lists all the general ledger accounts and their balances at a specific point in time. While the trial balance does not provide a summary of income and expenses, it serves as a foundation for preparing the P&L. It ensures that total debits equal total credits, which is essential for accurate financial reporting.
The statement of comprehensive income expands on the P&L by including other comprehensive income items. This document captures revenues, expenses, gains, and losses that are not realized in the income statement. By presenting a broader view of financial performance, it helps stakeholders understand the overall economic changes affecting the company.
The income tax return shares similarities with the P&L as both documents report income and expenses. However, the tax return is specifically designed for tax purposes, detailing how much income is taxable and what deductions are claimed. Understanding the relationship between the two can help businesses optimize their tax strategies while ensuring compliance with regulations.
The financial forecast is akin to the P&L in that it projects future revenues and expenses based on historical data and market trends. While the P&L reflects past performance, the financial forecast helps businesses plan for the future. This document is critical for setting goals and making informed decisions about investments and resource allocation.
Form Specifications
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Profit and Loss form is used to summarize the revenues, costs, and expenses incurred during a specific period. It helps businesses assess their financial performance. |
| Components | This form typically includes sections for total revenue, cost of goods sold, gross profit, operating expenses, and net profit or loss. |
| Frequency | Businesses often prepare this form on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis to track financial progress over time. |
| State-Specific Requirements | In some states, specific formats or additional information may be required by state laws. For example, California requires adherence to the California Corporations Code. |
| Importance for Stakeholders | Investors, creditors, and management rely on the Profit and Loss form to make informed decisions regarding the business's financial health. |
Different PDF Templates
Boyfriend Applications - Share any inside jokes you have with your boyfriend.
96well Plate - Simple and efficient layout for easy data entry.
The Georgia WC-100 form is essential for those seeking resolution in workers' compensation claims and can be found through resources like Georgia PDF Forms, which assist in navigating the mediating process effectively.
Employee Advance Form - Submit a request for a salary advance payment.
Sample - Profit And Loss Form
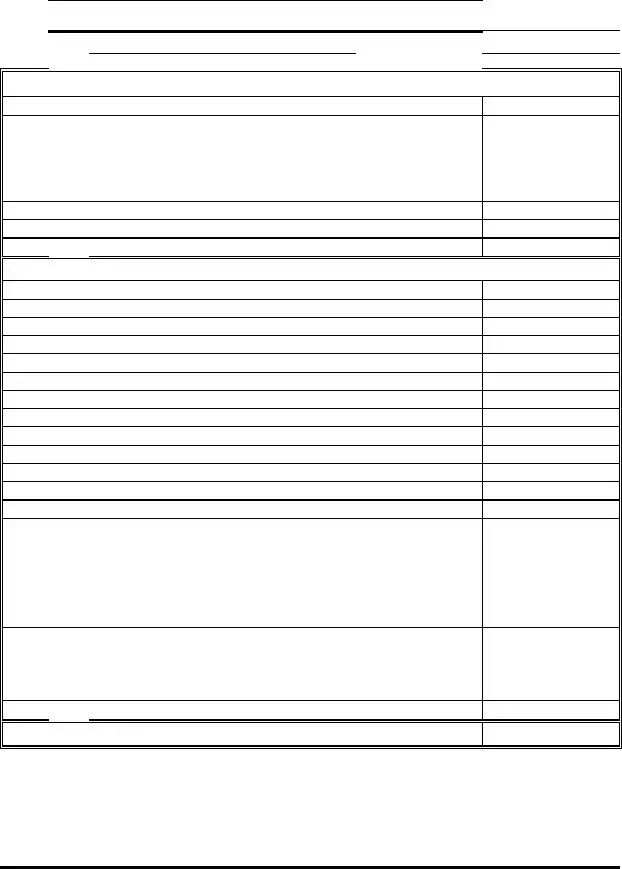
MONTHLY PROFIT & LOSS STATEMENT
FOR |
(business name) |
Month |
Year |
(Business Expenses are set forth below - Personal Expenses are Not Included)
|
|
|
! |
INCOME |
1 |
Gross Receipts or Sales |
|
||
2 |
Cost of Goods Sold |
|
||
|
(a) |
Purchases |
|
|
|
(b) |
Cost of Labor (not including salaries or employment |
||
|
benefits or tax) |
|
|
|
|
(c) |
Materials and Supplies |
|
|
3 |
Gross Profit |
|
|
|
4 |
Other Income |
|
|
|
5 |
Gross Income |
EXPENSES (not including Ch 13 Plan Payment) |
||
|
|
! |
||
6 |
Business Property Rent or Lease |
|
||
7 |
Salaries and Wages of Employees |
|
||
8 |
Employee Benefits |
|
|
|
9 |
Equipment Lease Payments |
|
||
10 |
Secured Debt Payments (Not included in plan) |
|
||
11 |
Supplies (not included in 2(c)) |
|
||
12 |
Utilities |
|
|
|
13 |
Telephone |
|
|
|
14 |
Repairs and Maintenence |
|
||
15 |
Miscellaneous Office Expense |
|
||
16 |
Advertising |
|
|
|
17 |
Travel and Entertainment |
|
||
18 |
Professional Fees |
Name:__________ Purpose:_______________ |
||
19 |
Insurance |
|
|
|
|
(a) |
Liability |
|
|
|
(b) |
Property |
|
|
|
(c) |
Vehicle |
|
|
|
(d) |
Worker's Compensation |
|
|
|
(e) |
Other ___________________ |
|
|
20 |
Taxes |
|
|
|
|
(a) |
Payroll |
|
|
|
(b) |
Sales |
|
|
|
(c) |
Other ___________________ |
|
|
21 |
Total Business Expenses |
|
||
|
! |
TOTAL PROFIT (LOSS) (line 5 minus line 21) |
||
I/We declare under penalty of purjury that the information provided is true and correct to the best of my/our knowledge, information and belief
Dated:
Debtor(s) Signature
